What’s New in Certified Ethical Hacker v13 AI ( CEH v13 AI)?
Explore the latest updates in Certified Ethical Hacker v13 (CEH v13 AI). Discover the new features and enhancements, including AI-driven cybersecurity tools, expanded cloud security modules, and advanced IoT protection. Learn how CEH v13 improves upon previous versions and how it integrates AI to address modern cyber threats. Stay informed about the newest developments in ethical hacking and how CEH v13 can enhance your cybersecurity skills. CEH v13 AI, Certified Ethical Hacker v13, what's new in CEH v13, CEH v13 updates, AI in cybersecurity, CEH v13 features, ethical hacking v13, CEH v13 certification, AI-driven ethical hacking, CEH v13, Certified Ethical Hacker v13 AI, CEH v13 AI, CEH v13 training, CEH v13 certification, AI in ethical hacking, CEH v13 course, CEH v13 exam, ethical hacking certification, AI cybersecurity training, CEH v13 updates

What’s New in Certified Ethical Hacker v13 AI ( CEH v13 AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Cybersecurity : A Revolution in Ethical Hacking
Artificial Intelligence (AI) in cybersecurity refers to the use of machine learning algorithms, data analytics, and other AI technologies to enhance security measures and protect systems from cyber threats. AI technologies analyze vast amounts of data to identify patterns, detect anomalies, and respond to potential threats more efficiently than traditional methods. Here are some key aspects of AI in cybersecurity:
1. Threat Detection and Prevention
- Anomaly Detection: AI systems can analyze network traffic and user behavior to identify unusual patterns that might indicate a security breach. By learning from historical data, AI can detect anomalies that deviate from normal activity, such as unusual login times or data access patterns.
- Malware Detection: AI-driven tools use machine learning algorithms to recognize and classify new and evolving malware based on its behavior and characteristics. This approach allows for the identification of threats that traditional signature-based systems might miss.
2. Automated Response and Mitigation
- Incident Response: AI can automate responses to detected threats, such as isolating affected systems, blocking malicious IP addresses, or initiating predefined response protocols. This rapid response can minimize the impact of security incidents and reduce the time required for manual intervention.
- Vulnerability Management: AI tools can continuously scan systems for vulnerabilities, assess their severity, and prioritize remediation efforts. This proactive approach helps organizations address weaknesses before they can be exploited by attackers.
3. Advanced Threat Intelligence
- Predictive Analytics: AI can analyze historical and real-time data to predict potential threats and vulnerabilities. By identifying trends and patterns, AI can help organizations anticipate future attacks and implement preventive measures.
- Threat Intelligence Integration: AI systems can aggregate and analyze threat intelligence from various sources, providing insights into emerging threats and attack vectors. This integrated approach enhances situational awareness and helps security teams stay ahead of evolving threats.
4. Behavioral Analysis and User Authentication
- Behavioral Analytics: AI can monitor user behavior to detect deviations from normal patterns, such as unusual access requests or abnormal data transfers. This helps in identifying compromised accounts or insider threats.
- Adaptive Authentication: AI-driven systems can implement adaptive authentication methods that adjust security measures based on the context of the user’s behavior and access patterns. This approach ensures a higher level of security while maintaining user convenience.
5. Security Operations Optimization
- Security Information and Event Management (SIEM): AI enhances SIEM systems by automating the analysis of security events and reducing false positives. AI algorithms can correlate data from various sources to identify and prioritize significant security incidents.
- Threat Hunting: AI tools can assist security professionals in proactively searching for hidden threats within their networks. By analyzing large volumes of data and identifying potential indicators of compromise, AI supports more effective threat hunting efforts.
6. Challenges and Considerations
- Data Privacy: The use of AI in cybersecurity involves analyzing sensitive data, raising concerns about privacy and data protection. Organizations must ensure that AI systems comply with relevant privacy regulations.
- False Positives: While AI can reduce false positives compared to traditional methods, it is not infallible. Continuous tuning and monitoring are required to balance sensitivity and specificity in threat detection.
AI in cybersecurity represents a significant advancement in protecting systems against sophisticated threats. By leveraging AI technologies, organizations can enhance their security posture, respond to incidents more effectively, and stay ahead of emerging cyber threats.
CEH v13 AI Official Release Date is 23rd September 2024
What is CEH v13 AI?
CEH v13 AI (Certified Ethical Hacker version 13) is the latest iteration of the Certified Ethical Hacker certification offered by EC-Council, with a focus on integrating artificial intelligence (AI) into the field of ethical hacking and cybersecurity.
1. Integration of AI in CEH v13
AI-Driven Techniques: CEH v13 AI introduces new tools and techniques that leverage AI to enhance ethical hacking practices. This includes AI-driven penetration testing, where machine learning algorithms assist in identifying vulnerabilities and exploiting them to test system defenses.
Machine Learning for Threat Detection: The certification emphasizes the use of machine learning models for threat detection and response. AI algorithms are employed to analyze large volumes of data, detect anomalies, and predict potential security threats based on patterns and historical data.
2. Key Features of CEH v13 AI
Updated Curriculum: CEH v13 AI includes updated modules that focus on the integration of AI in various cybersecurity domains. This includes AI-enhanced tools for penetration testing, cloud security, IoT security, and advanced malware analysis.
Expanded Coverage: The certification offers expanded coverage of cloud security and IoT security, reflecting the growing importance of these areas in the modern cybersecurity landscape. AI techniques are applied to address vulnerabilities and enhance the security of cloud environments and Internet of Things (IoT) devices.
Advanced Malware Analysis: CEH v13 AI introduces advanced methods for malware analysis using AI. This includes the use of machine learning to detect and analyze new and evolving malware threats, providing a more comprehensive approach to malware defense.
5 Phases of the Ethical Hacking Framework Enhanced by AI
Ethical hacking follows a systematic process typically divided into five phases: reconnaissance, scanning, gaining access, maintaining access, and covering tracks. With the integration of AI, these stages are significantly enhanced, making ethical hacking more precise, efficient, and effective. The CEH v13 AI framework incorporates advanced AI-powered tools to elevate each phase, allowing ethical hackers to simulate real-world hacking scenarios with greater accuracy. Here’s how AI enhances each stage of the ethical hacking process:
-
Reconnaissance: This initial phase involves gathering information about the target to identify potential vulnerabilities. AI-powered tools can analyze vast amounts of data from various sources, providing ethical hackers with detailed insights into potential weaknesses. AI algorithms can detect patterns, anomalies, and indicators of vulnerabilities, enabling hackers to better understand the target’s security posture.
-
Scanning: AI accelerates the scanning phase by automating the detection of vulnerable services, open ports, and other security gaps. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, AI can quickly identify potential points of entry and prioritize them based on risk levels. This ensures that no attack vector is overlooked and that the scanning process is thorough and efficient.
-
Gaining Access: In this phase, the goal is to exploit identified vulnerabilities to gain unauthorized access to the target system. AI enhances this stage by automating complex attack strategies and adapting to security defenses in real-time. Ethical hackers can use AI to execute sophisticated exploitation techniques, bypassing security measures with a higher success rate while minimizing detection risks.
-
Maintaining Access: Once access is gained, the next step is to maintain a foothold within the compromised system. AI helps in maintaining a low profile by continuously analyzing system behaviors and adjusting tactics to avoid detection. It ensures that the access remains undetected by adapting to changes in the environment and utilizing stealth techniques to keep the connection intact.
-
Covering Tracks: The final phase involves erasing evidence of the hacking activity to prevent detection by security teams. AI-powered tools can automate the process of cleaning logs, modifying timestamps, and deleting traces of the attack, ensuring that the intrusion remains hidden. AI’s ability to mimic legitimate user behavior further complicates detection efforts, making it challenging for defenders to trace the attack back to its source.
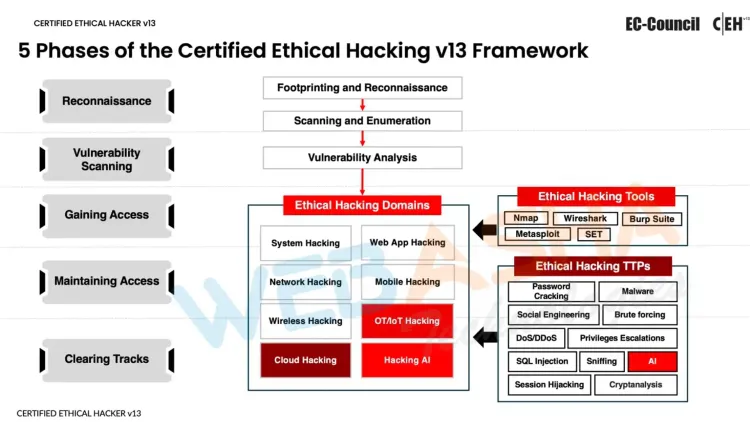
By mastering these AI-enhanced phases, ethical hackers can effectively simulate the tactics used by cyber attackers, providing valuable insights into an organization's vulnerabilities. This AI-driven approach makes ethical hackers indispensable to modern cybersecurity teams, as they can anticipate and counteract the advanced methods employed by malicious actors.
Hacking AI Systems: OWASP Top 10 Attacks
As AI technologies become deeply integrated into corporate operations, they have increasingly become prime targets for cyberattacks. The CEH v13 AI training includes a dedicated module on hacking AI systems, focusing on the OWASP Top 10 vulnerabilities that are specific to AI. This module equips ethical hackers with the skills needed to identify, exploit, and secure AI systems against these emerging threats.
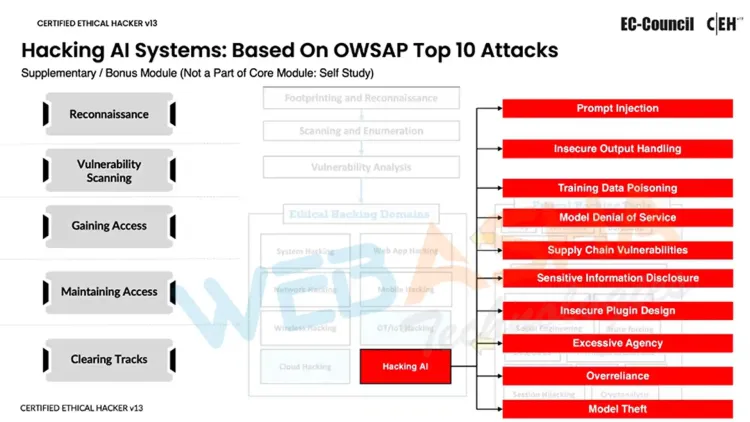
At WebAsha Technologies, we ensure that students not only learn to identify these AI-specific vulnerabilities but also understand how to exploit and defend against them effectively. As AI continues to be adopted across various industries, possessing these skills is vital for cybersecurity professionals. With AI systems being targeted more frequently, staying ahead of these threats is essential in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity. This specialized training empowers ethical hackers to safeguard AI systems, making them invaluable assets in protecting organizations from potential AI-targeted attacks.
ShellGPT: Your AI-Driven Scripting Assistant
One of the most significant advancements in the CEH v13 AI framework is the integration of ShellGPT, an AI-powered scripting tool designed to streamline and automate many of the repetitive tasks involved in ethical hacking. ShellGPT enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of ethical hackers by:
-
Generating Shell Commands with Minimal Effort: ShellGPT simplifies the creation of shell commands, allowing ethical hackers to generate accurate and effective commands with minimal input. This reduces the manual effort required and speeds up the overall process of executing tasks.
-
Automating Script Creation for Attack Simulations: ShellGPT automates the generation of scripts used in attack simulations, eliminating the need for manual script writing. This automation ensures that attack simulations are executed quickly and accurately, providing valuable insights into potential vulnerabilities.
-
Simplifying Complex Hacking Tasks with Natural Language Inputs: With ShellGPT, ethical hackers can use natural language to describe complex tasks. The AI then translates these descriptions into the appropriate commands or scripts, making it easier to perform sophisticated hacking operations without needing to memorize complex syntax.
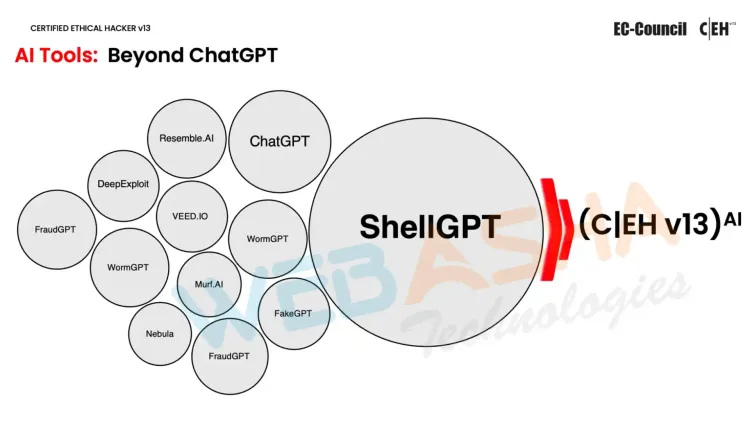
By leveraging ShellGPT, ethical hackers can shift their focus from repetitive, manual tasks to more advanced strategies and problem-solving techniques. This AI-driven tool not only enhances productivity but also allows cybersecurity professionals to tackle more complex challenges with greater efficiency and precision.
Difference Between CEH v11, CEH v12 and CEH v13 AI
|
|
CEH v11 |
CEH V12 |
CEH v13 AI |
|
Total Number of Modules |
20 |
20 |
20 |
|
Total Number of Slides |
1640 |
1676 |
1266 |
|
Total Number of Labs |
200 |
220 |
221 (91 Core Labs + 130 self study labs available on upgrade) |
|
Total Number of New Labs |
92 |
33 |
130 |
|
Attack Techniques |
420 |
519 |
550 |
|
New Technology Added |
OT Technology, Serverless Computing, WPA3 Encryption, APT, Fileless Malware, Web API, and Web Shell |
MITRE ATT&CK Framework, Diamond Model of Intrusion Analysis, Techniques for Establishing Persistence, Evading NAC and Endpoint Security, Fog Computing, Edge Computing, and Grid Computing |
Al-Driven Ethical Hacking, Zero Trust Architecture, Active Directory Attacks, Ransomware Attacks and Mitigation, Cloud Security, Al and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity, IoT Security Challenges, Critical Infrastructure Vulnerabilities, Deepfake Threats, Extended Detection and Response (XDR), Quantum Computing Risks and Attacks, Post-Quantum Cryptography |
|
OS Used for Labs |
Windows 10, Windows Server Windows 11, Windows Server 2019, Parrot Security, Android, Ubuntu Linux |
Windows 10, Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Parrot Security, Android, Ubuntu Linux
|
Windows 11, Windows Server 2022, Windows Server 2019, Parrot Security, Android, Ubuntu Linux |
|
Exam |
125 Questions (MCO) |
125 Questions (MCO) |
125 Questions (MCO) |
|
Exam Duration |
4 Hours |
4 Hours |
4 Hours |
|
Exam Delivery |
VUE / ECCEXAM |
VUE / ECCEXAM |
VUE / ECCEXAM |
|
NICE Compliance |
Final NICE 2.0 Framework |
Final NICE 2.0 Framework |
Final NICE 2.0 Framework |
CEH v13 AI Technologies Updates
Active Directory Attacks
Active Directory attacks target the central identity management system used in many organizations, aiming to gain unauthorized access to network resources. Common techniques include credential theft, privilege escalation, and exploiting misconfigurations.
Zero Trust Architecture
Zero Trust Architecture is a security model that assumes no user or device, whether inside or outside the network, should be trusted by default. It requires continuous verification of identities and strict access controls to protect sensitive data and systems.
Ransomware Attacks and Mitigation
Ransomware attacks involve malicious software that encrypts data, with attackers demanding a ransom to restore access. Mitigation strategies include regular backups, robust security protocols, user training, and the use of advanced threat detection tools.
Deepfake Threats
Deepfake threats involve the use of AI-generated synthetic media to create realistic but fake videos, images, or audio. These can be used for disinformation, fraud, and other malicious activities, posing significant challenges to cybersecurity and digital trust.
IoT Security Challenges
IoT security challenges stem from the vast number of interconnected devices with varying security standards. Common issues include weak authentication, insufficient encryption, and vulnerabilities that can be exploited to access networks or steal data.
Critical Infrastructure Vulnerabilities
Critical infrastructure vulnerabilities are weaknesses in essential systems like power grids, water supplies, and transportation networks. These vulnerabilities can be exploited by cyber attackers, leading to disruptions that have widespread and potentially catastrophic impacts.
Cloud Security
Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and services in cloud environments from cyber threats. Key aspects include securing cloud configurations, managing access controls, and defending against data breaches and unauthorized access.
Extended Detection and Response (XDR)
Extended Detection and Response (XDR) is a security approach that integrates data from multiple security tools to provide comprehensive threat detection and response capabilities across an organization’s entire IT environment, including endpoints, networks, and servers.
Quantum Computing Risks and Threats
Quantum computing poses risks to traditional cryptographic methods, as its immense processing power could break current encryption standards. This potential capability threatens data security, requiring new approaches to encryption and cybersecurity defenses.
Post-Quantum Cryptography
Post-Quantum Cryptography involves developing cryptographic algorithms that are resistant to the capabilities of quantum computers. It aims to protect data against future quantum-based attacks, ensuring the continued security of encrypted information.
AI and Machine Learning in Cybersecurity
AI and Machine Learning are transforming cybersecurity by enabling automated threat detection, predictive analysis, and more sophisticated defense mechanisms. These technologies help in identifying patterns, detecting anomalies, and responding to cyber threats in real time.
CEH V13 AI Certification Updates
Gain More with CEH v13 AI
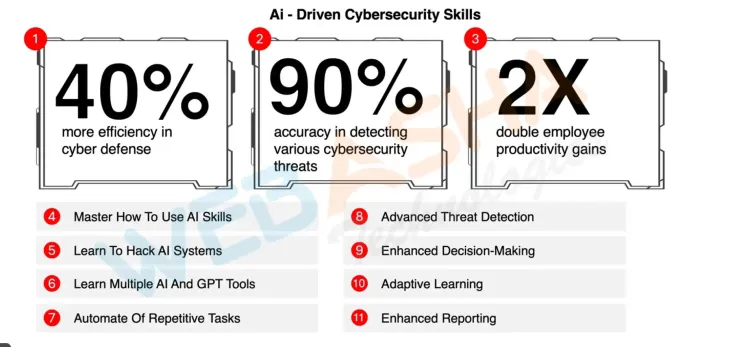
CEH v13 Curriculum
- Module 01: Introduction to Certified Ethical Hacking - CEH v13 AIL
- Cover the basics of key issues within the information security world, as well as the fundamentals of ethical hacking, data security controls, relevant laws, and standard procedures.
- Module 02: Foot printing and reconnaissance
- Learn how to use the newest techniques and tools to perform foot printing and reconnaissance, a important pre-attack part of the ethical hacking method.
- Module 03: Scanning Networks
- Learn completely different network scanning techniques and countermeasures.
- Module 04: Enumeration
- Learn various enumeration techniques, like Border gateway Protocol (BGP) and Network File Sharing (NFS) exploits, and associated countermeasures.
- Module 05: Vulnerability Analysis
- Learn how to spot security loopholes in a target organization’s network, communication infrastructure, and finish systems.
- Module 06: System Hacking
- Learn about the various system hacking methodologies—including steganography, steganalysis attacks, and covering tracks—used to find system and network vulnerabilities.
- Module 07: Malware Threats
- Get an introduction to the various forms of malware, like Trojans, viruses, and worms, as well as system auditing for malware attacks, malware analysis, and countermeasures.
- Module 08: Sniffing
- Learn about packet-sniffing techniques and the way to use them to find network vulnerabilities, as well as countermeasures to defend against sniffing attacks.
- Module 09: Social Engineering
- Learn social engineering concepts and techniques, as well as a way to determine theft makes an attempt, audit human-level vulnerabilities, and recommend social engineering countermeasures.
- Module 10: Denial-of-Service
- Learn about completely different Denial of Service (DoS) and Distributed DoS (DDoS) attack techniques, as well because the tools wont to audit a target and devise DoS and DDoS countermeasures and protections.
- Module 11: Session Hijacking
- Understand the various session hijacking techniques wont to discover network-level session management, authentication, authorization, and cryptographic weaknesses and associated countermeasures.
- Module 12: Evading IDS, Firewalls, and Honeypots
- Get introduced to firewall, intrusion detection system, and honeypot evasion techniques; the tools wont to audit a network perimeter for weaknesses; and countermeasures.
- Module 13: Hacking net Servers
- Learn about web server attacks, as well as a comprehensive attack methodology wont to audit vulnerabilities in web server infrastructures and countermeasures.
- Module 14: Hacking web Applications
- Learn about web application attacks, as well as a comprehensive web application hacking methodology wont to audit vulnerabilities in web applications and countermeasures.
- Module 15: SQL Injection
- Learn about SQL injection attack techniques, injection detection tools, and countermeasures to find and defend against SQL injection makes an attempt.
- Module 16: Hacking Wireless Networks
- Learn about wireless encryption, wireless hacking methodologies and tools, and Wi-Fi security tools.
- Module 17: Hacking Mobile Platforms
- Learn about mobile platform attack vectors, android vulnerability exploits, and mobile security pointers and tools.
- Module 18: IoT Hacking
- Learn how to secure and defend net of Things (IoT) and operational technology (OT) devices and possible threats to IoT and OT platforms.
- Module 19: Cloud Computing
- Learn completely different cloud computing ideas, like container technologies and server less computing, numerous cloud-based threats and attacks, and cloud security techniques and tools.
- Module 20: Cryptography
- In the final module, study cryptography and ciphers, public-key infrastructure, cryptography attacks, and cryptanalysis tools.
SKILLS LEARNED IN CEH v13 AI SUPPORT 49+ CYBERSECURITY JOB ROLES
Skills Learned in the CEH Are Mapped to 49 Cybersecurity Job Roles
Based on Our Job Task Analysis and Real Job Requirements Posted by Organizations on Job Portals
Job Roles Increased from 20 to 49
- Mid-Level Information Security Auditor
- Cybersecurity Auditor
- Security Administrator
- IT Security Administrator
- Information Security Analyst 1
- Infosec Security Administrator
- Cybersecurity Analyst level 1, level 2, & level 3
- Network Security Engineer
- SOC Security Analyst
- Network Engineer
- Senior Security Consultant
- Information Security Manager
- Senior SOC Analyst
- Solution Architect
- Cybersecurity Consultant
- Cyber Defense Analyst
- Vulnerability Assessment Analyst
- Warning Analyst
- All-Source Analyst
- Cyber Defense Incident Responder
- Research & Development Specialist
- Senior Cloud Security Analyst
- Third Party Risk Management
- Threat Hunting Analyst
- Penetration tester
- Cyber Delivery Manager
- Application Security Risk
- Threat Modelling Specialist
- Web Application Penetration Testing
- SAP Vulnerability Management - Solution Deliv Advisor
- Ethical Hacker
- SIEM Threat Responder
- Product Security Engineer / Manager
- Endpoint Security Engineer
- Cybersecurity Instructor
- Red Team Specialist
- Data Protection & Privacy Officer
- SOAR Engineer
- Al Security Engineer
- Sr. IAM Engineer
- PCI Security Advisor
- Exploitation Analyst (EA)
- Zero Trust Solutions Engineer / Analyst
- Cryptographic Engineer
- AI/ML Security Engineer
- Machine Learning Security Specialist
- Al Penetration Tester
- AI/ ML Security Consultant
- Crypto Security Consultant
CEH v13 AI Brings New Opportunities: Jobs and Salary Insights
The latest version of the Certified Ethical Hacker certification, CEH v13 AI, brings a wealth of new opportunities in the cybersecurity field, thanks to its focus on AI-driven techniques and modern security practices. The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in CEH v13 not only enhances the skills of cybersecurity professionals but also opens doors to advanced roles that are in high demand. Below, we explore the potential job roles and the corresponding salary ranges for CEH v13 AI-certified professionals in both INR (Indian Rupees) and USD (United States Dollars).
1. Career Opportunities with CEH v13 AI
CEH v13 AI certification equips professionals with cutting-edge skills in ethical hacking, AI-driven threat detection, cloud security, IoT protection, and more. These skills are highly sought after in the cybersecurity job market, leading to roles such as:
- Penetration Tester
- Security Analyst
- Cybersecurity Consultant
- AI Security Specialist
- Cloud Security Expert
- IoT Security Specialist
- Malware Analyst
2. Salary Expectations for CEH v13 AI-Certified Professionals
The table below provides an overview of the expected salary ranges for various job roles in cybersecurity for professionals holding CEH v13 AI certification. Salaries vary based on experience, location, and the specific requirements of the role.
| Job Role | Average Salary (INR) | Average Salary (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Penetration Tester | ₹600,000 - ₹1,500,000 | $70,000 - $110,000 |
| Security Analyst | ₹500,000 - ₹1,200,000 | $60,000 - $90,000 |
| Cybersecurity Consultant | ₹800,000 - ₹2,000,000 | $80,000 - $120,000 |
| AI Security Specialist | ₹1,000,000 - ₹2,500,000 | $90,000 - $130,000 |
| Cloud Security Expert | ₹900,000 - ₹2,200,000 | $85,000 - $125,000 |
| IoT Security Specialist | ₹800,000 - ₹1,800,000 | $75,000 - $115,000 |
| Malware Analyst | ₹700,000 - ₹1,500,000 | $65,000 - $105,000 |
3. Key Factors Influencing Salaries
- Location: Salaries vary significantly between regions, with major tech hubs offering higher compensation.
- Experience Level: Professionals with more experience or additional certifications can command higher salaries.
- Industry Demand: High-demand industries like finance, healthcare, and government often offer premium pay for skilled cybersecurity professionals.
- Specialized Skills: Expertise in AI, cloud security, and advanced penetration testing techniques increases marketability and earning potential.
CEH v13 AI Training with Certification at WebAsha Technologies
In today’s rapidly evolving cybersecurity landscape, staying ahead of cyber threats requires more than just foundational knowledge. It demands expertise in cutting-edge technologies, including Artificial Intelligence (AI). WebAsha Technologies proudly offers the CEH v13 AI Training and Certification program, designed to equip cybersecurity professionals with the advanced skills needed to tackle modern challenges. Whether you're a beginner or an experienced professional, this course will prepare you to excel in the field of ethical hacking with a focus on AI-driven security practices.
Why Choose CEH v13 AI with WebAsha Technologies?
At WebAsha Technologies, we understand the importance of staying updated with the latest cybersecurity trends and technologies. Our CEH v13 AI Training program is tailored to provide you with comprehensive knowledge and hands-on experience in ethical hacking, with a special emphasis on AI integration. Here’s why WebAsha is your ideal training partner:
-
Accredited Training Provider: As an EC-Council Accredited Training Center, WebAsha Technologies ensures that you receive top-quality education aligned with industry standards. Our curriculum is updated to reflect the latest CEH v13 AI enhancements, providing you with the skills that are in demand.
-
Expert Instructors: Learn from experienced instructors who are industry professionals with real-world expertise in cybersecurity and AI. Our trainers are dedicated to helping you understand complex concepts and guiding you through practical applications.
-
Comprehensive Curriculum: The CEH v13 AI course covers a wide range of topics, including AI-driven penetration testing, advanced malware analysis, cloud security, and IoT protection. Our curriculum is designed to give you a well-rounded understanding of both traditional and modern ethical hacking techniques.
-
Hands-On Labs and Real-World Simulations: At WebAsha Technologies, we believe in learning by doing. Our training includes access to state-of-the-art lab environments where you can practice ethical hacking techniques in real-world scenarios. AI-based simulation tools are used to provide a realistic and immersive learning experience.
-
Flexible Learning Options: We offer flexible learning modes, including online, in-person, and hybrid classes. Choose from weekday, weekend, or evening batches to fit your schedule. Our goal is to make learning accessible and convenient for all students, whether you are a working professional or a full-time student.
Key Features of the CEH v13 AI Training Program
- AI-Powered Security Tools: Gain insights into the use of AI in cybersecurity, including AI-driven penetration testing tools and machine learning for threat detection.
- Cloud and IoT Security: Learn the latest best practices for securing cloud environments and IoT devices, reflecting the growing importance of these areas in today’s digital landscape.
- Advanced Malware Analysis: Explore new methods for detecting and neutralizing malware using AI techniques, preparing you to defend against evolving threats.
- Updated Exam Preparation: Prepare for the CEH v13 AI certification exam with the latest study materials, practice tests, and expert guidance. Our training includes tips on time management and strategies for tackling practical exam questions.
CEH v13 AI Certification Exam
The CEH v13 AI certification exam is a comprehensive test that evaluates your understanding of AI-driven cybersecurity practices, ethical hacking techniques, and the ability to apply this knowledge in real-world scenarios. WebAsha Technologies provides full support in preparing for this exam, including access to study guides, practice exams, and personalized mentoring.
Benefits of Earning Your CEH v13 AI Certification with WebAsha Technologies
- Enhanced Skills and Knowledge: Master AI integration in ethical hacking and gain a competitive edge in the cybersecurity job market.
- Career Advancement: Increase your job prospects and earning potential with a globally recognized certification. Roles such as penetration tester, security analyst, and cybersecurity consultant are just a few of the opportunities available to CEH v13 AI certified professionals.
- Continuous Support and Resources: After completing your certification, WebAsha Technologies offers ongoing support through job placement assistance, networking opportunities, and access to additional learning resources.
Success Stories and Testimonials
Our students’ success is our greatest achievement. Many of our CEH v13 AI certified professionals have gone on to secure prominent positions in top companies, leveraging their skills to make impactful contributions to the cybersecurity field. Hear from our alumni about how WebAsha Technologies helped them achieve their career goals.
Get Started with WebAsha Technologies Today!
Don’t miss the opportunity to advance your career with CEH v13 AI Training and Certification. Join WebAsha Technologies and become part of a community of cybersecurity professionals committed to excellence and continuous learning.
Contact us today to learn more about our CEH v13 AI course, schedules, fees, and registration details. Let WebAsha Technologies be your partner in mastering the future of cybersecurity!











![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)

![[2025] Top 100+ VAPT Interview Questions and Answers](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/image_100x75_6512b1e4b64f7.jpg)









