What is Machine Learning Algorithms? How does Machine Learning Work and its Types?
As you know, we are living in the world of human beings and machines. Humans have been evolving and learning from their past experience for millions of years ago. On the opposite hand, The new era of robots and machines have just begun. Now you’ll be able to think about it in a way that presently we tend to live within the primitive age of machines, while the future of machine is enormous and is beyond the scope of our imagination.

Machine Learning For Beginners
Have you ever shopped online? So while checking for a product online, have you noticed it recommending a product similar to what you are looking for? Or did you notice that “people bought this product also bought this” combination of products?. How are they providing these recommendations to us? This is because of machine learning.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a subset of artificial intelligence which focuses mainly on learning and making predictions based on the machine’s experiences.
What does it do?
It enables the computers to make data-driven decisions rather than being explicitly programmed for carrying out a certain task. These algorithms are designed in a way that they learn and improve over time when are exposed to new data.
What is Machine Learning – Evolution of Machines
As you know, we are living in the world of human beings and machines. Humans have been evolving and learning from their past experience for millions of years ago. On the opposite hand, The new era of robots and machines have just begun. Now you’ll be able to think about it in a way that presently we tend to live within the primitive age of machines, while the future of machine is enormous and is beyond the scope of our imagination.
In today’s world, the machines have to be programmed before they start following our instructions. But what if the machine started learning on their own from their experience feel like us, work like us, do things more accurately than us?
How does Machine Learning Work?
Machine Learning algorithm is created using training datasets to create a new model. When new input file is introduced to the ml algorithmic program, it makes predictions on the basis of the model.
The prediction is evaluated for the accuracy and if the accuracy is acceptable, the ML algorithm is deployed. If the accuracy isn’t acceptable, the Machine Learning algorithm is trained again with an augmented training dataset.
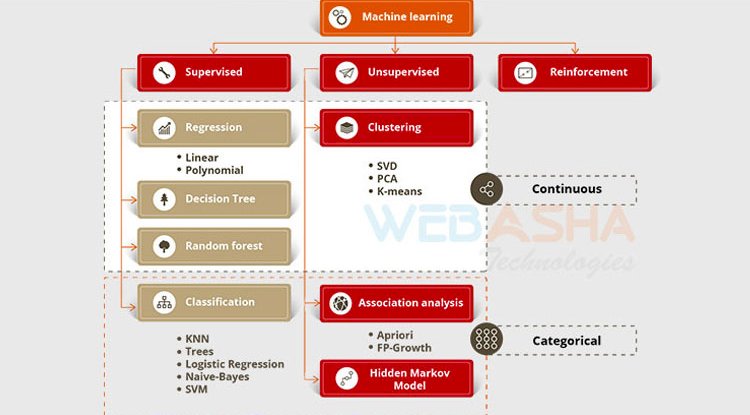
Types of Machine Learning
Machine learning is sub-categorized to three types:
Supervised Learning – Train-Me!
Unsupervised Learning – I am self-sufficient in the learning
Reinforcement Learning – My life My rules! (Hit & Trial)
What is Supervised Learning?
Supervised Learning is, where you can consider the learning is guided by a teacher. We have a dataset that acts as an educator and its role is to train the models or the machines. Once the model gets trained it will begin creating predictions or decisions once data is given to that.
What is Unsupervised Learning?
The model learns through observations and finds structures in the data. Once the model is given a dataset, it automatically finds relationships and patterns in the dataset by creating clusters in it. What it cannot do is add labels to the cluster, like it cannot say this a group of oranges or mangoes, but it will separate all the oranges from mangoes.
Let’s say we tend to given pictures of oranges, bananas, and mangoes to this model, so what it does is, based on some patterns and relationships it creates several clusters and then divides the datasets into those clusters. Now if a new data is provided to these models, it adds it to one of the clusters which was created.
What is Reinforcement Learning?
It is the ability of an agent to interact with the environment and find out which is the best outcome. It follows the conception of trial and hit methodology. The agent is rewarded or punished with some extent for an accurate or a wrong answer, and on the basis of the positive reward points gained, the model trains itself and it gets able to predict the new knowledge given to it.
Machine Learning Algorithms
Naïve Bayes Classifier Algorithm (Supervised Learning – Classification)
The Naïve Bayes classifier is predicated on Bayes’ theorem and classifies each value as independent of the other value. It permits us to predict a class/category, based on a given set of features, using probability.
Despite its simplicity, the classifier does surprisingly well and is often used due to the fact it outperforms more sophisticated classification methods.
K Means Clustering Algorithm (Unsupervised Learning – Clustering)
The K Means Clustering algorithm is a type of unsupervised learning, which is used to categorise unlabelled data, i.e. data without defined categories or groups. The algorithmic program works by finding teams inside the information, with the number of teams represented by the variable K. It then works iteratively to assign each data point to one of K groups based on the features provided.
Support Vector Machine Algorithm (Supervised Learning – Classification)
Support Vector Machine algorithms are supervised learning models that analyse information used for classification and regression analysis. They basically filter information into categories, that is achieved by providing a collection of training examples, every set marked as belonging to at least one or the opposite of the 2 categories. The algorithm then works to build a model that assigns new values to one category or the other.
Linear Regression (Supervised Learning/Regression)
Linear regression is that the most elementary sort of regression. Simple linear regression allows us to understand the relationships between two continuous variables.
Logistic Regression (Supervised learning – Classification)
Logistic regression focuses on estimating the probability of a happening occurring based on the previous information provided. It is wont to cover a binary variable quantity, that is where only two values, 0 and 1, represent outcomes.
Artificial Neural Networks (Reinforcement Learning)
An artificial neural network (ANN) comprises ‘units’ arranged in a series of layers, each of which connects to layers on either side. ANNs are impressed by biological systems, like the brain, and how they process information. ANNs are essentially a large number of interconnected processing elements, working in unison to solve specific problems.
ANNs also learn by example and through experience, and they are extremely useful for modelling non-linear relationships in high-dimensional data or where the relationship amongst the input variables is difficult to understand.
Decision Trees (Supervised Learning – Classification/Regression)
A decision tree is a flow-chart-like tree structure that uses a branching method to illustrate every possible outcome of a decision. Each node among the tree represents a test on a selected variable – and every branch is that the outcome of that test.
Random Forests (Supervised Learning – Classification/Regression)
Random forests or ‘random decision forests’ is an ensemble learning technique, combining multiple algorithms to generate better results for classification, regression and other tasks. Each individual classifier is weak, but when combined with others, can produce excellent results. The algorithmic program starts with a ‘decision tree’ (a tree-like graph or model of decisions) and an input is entered at the highest. It then travels down the tree, with data being segmented into smaller and smaller sets, based on specific variables.
Nearest Neighbours (Supervised Learning)
The K-Nearest-Neighbour algorithmic program estimates however probably an information purpose is to be a member of 1 group or another. It essentially looks at the data points around a single data point to determine what group it is actually in. For example, if one point is on a grid and the algorithm is trying to determine what group that data point is in (Group A or Group B, for example) it’d check out the information points close to it to check what group the bulk of the points are in.
Clearly, there are loads of things to think about once it involves selecting the correct machine learning algorithms for your business’ analytics. However, you don’t need to be a data scientist or expert statistician to use these models for your business. At WebAsha Technologies, our products and solutions utilise a comprehensive selection of machine learning algorithms, helping you to develop a process that can continuously deliver value from your data.











![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)



![[2025] Top 100+ VAPT Interview Questions and Answers](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/image_100x75_6512b1e4b64f7.jpg)







