The Role of Digital Forensics in Cybersecurity
Discover the crucial role of digital forensics in cybersecurity. Learn how digital forensic techniques help investigate cybercrimes, recover data, identify threats, and ensure legal compliance. Explore the steps, tools, and real-world applications of digital forensics in securing the digital world.

Introduction
In today’s digital era, cybersecurity breaches have become a growing concern for businesses, governments, and individuals alike. While preventive measures are vital, the role of digital forensics in identifying, investigating, and mitigating cyberattacks is equally critical. This article explores the fundamentals of digital forensics, its role in cybersecurity, and how it contributes to a secure digital landscape.
1. What is Digital Forensics?
Digital forensics is a specialized branch of forensic science that involves identifying, preserving, analyzing, and presenting electronic data. It plays a pivotal role in uncovering evidence related to cybercrimes such as hacking, data breaches, fraud, and even insider threats.
2. Types of Digital Forensic Investigations
Digital forensic investigations encompass a range of specialized areas, each targeting different aspects of digital forensics. Each type employs unique investigative techniques and tools to address specific challenges. From analyzing data traffic in networks to scrutinizing personal computers and investigating mobile devices to probing cloud storage, these diverse forensic fields collectively strengthen cybersecurity defenses and types of digital forensic investigatons are as follows:
a) Network Forensics
Network forensics is a critical branch of digital forensics focused on monitoring and analyzing computer network traffic for information gathering, legal evidence, or intrusion detection. This type of forensic investigation is vital in identifying and responding to cyber attacks, network breaches, and other security incidents. Network forensic specialists use various tools to capture and store network data, which is then meticulously analyzed to uncover unauthorized access, malicious activities, and sources of security threats. The insights gained from network forensics are vital for threat detection and ensuring the security of information systems.
b) Mobile Device Forensics
Mobile device forensics is a specialized field within digital forensics that deals with recovering and analyzing data from mobile devices, such as smartphones and tablets. Given the ubiquity of mobile devices, this branch of forensics plays a crucial role in modern investigations. Mobile forensics specialists focus on retrieving data like text messages, emails, photos, and application data from mobile devices, often working against the challenges posed by device encryption and the constant evolution of mobile operating systems. The evidence gathered from mobile devices can be pivotal in criminal and civil investigations.
c) Cloud Forensics
Cloud forensics is an emerging field in digital forensics, addressing the challenges of investigating data stored in cloud computing environments. As more organizations and individuals store data on cloud services, the need for cloud forensics has grown significantly. This type of forensic investigation involves analyzing data hosted on remote servers, including emails, documents, and complex databases. Cloud forensics specialists must navigate the intricacies of cloud architecture, dealing with issues like data sovereignty, multi-tenancy, and the distributed nature of cloud storage. The ability to effectively conduct cloud forensic investigations is becoming increasingly important as cloud services expand.
4. How Is Digital Forensics Used in an Investigation?
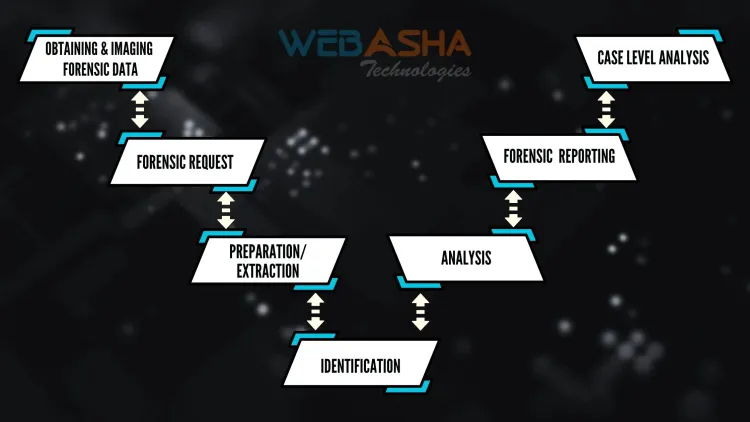
 5. Evidence Collection and Incident Analysis
5. Evidence Collection and Incident Analysis
When a security incident is suspected, the first step is to preserve the digital evidence. Digital forensics experts use specialised tools and techniques to ensure that data is collected in a forensically sound manner, preserving its integrity and authenticity. This evidence can include log files, memory dumps, network traffic captures, and system snapshots.
Once evidence is collected,digital forensics experts analyse it to reconstruct the timeline of events leading up to and during the incident. They identify the attack vectors, techniques, and tools used by the attackers. This analysis provides insight into the attacker’s methods and helps in understanding the scope of the breach.
Once the extent of the compromise is understood, digital forensics aids in devising strategies to contain the incident and prevent further damage. This might involve isolating compromised systems, removing malware, and closing exploited vulnerabilities.
Conclusion
Digital forensics is an indispensable pillar of cybersecurity, providing the tools and methodologies needed to combat modern cyber threats effectively. By enabling organizations to investigate and recover from attacks, digital forensics plays a vital role in building a secure and resilient digital ecosystem.
(FAQs)
1. What is digital forensics, and why is it important in cybersecurity?
Answer: Digital forensics is the process of collecting, preserving, analyzing, and presenting digital evidence from electronic devices. It’s vital in cybersecurity for investigating breaches, identifying perpetrators, and preventing future attacks.
2. How does digital forensics help in cybercrime investigations?
Answer: Digital forensics uncovers evidence of cybercrimes by analyzing compromised systems, tracing attack origins, and restoring lost data, which helps law enforcement build a case against offenders.
3. What are the primary steps involved in a digital forensics investigation?
Answer: The key steps include identification, preservation, analysis, documentation, and presentation of digital evidence. These ensure a structured approach to uncovering and preserving critical information.
4. What types of cybercrimes can digital forensics investigate?
Answer: Digital forensics can handle a wide range of cybercrimes, including hacking, phishing, ransomware attacks, insider threats, data breaches, and financial fraud.
5. What tools are commonly used in digital forensics?
Answer: Popular tools include EnCase, FTK (Forensic Toolkit), Autopsy, Cellebrite, and Wireshark. These tools assist in data recovery, analysis, and network traffic monitoring.
6. How does digital forensics ensure evidence is legally admissible in court?
Answer: By following strict protocols for evidence collection, chain of custody, and analysis, digital forensics ensures that the evidence is authentic, unaltered, and legally compliant.
7. Can digital forensics recover deleted or encrypted data?
Answer: Yes, advanced digital forensics tools and techniques can often recover deleted files and analyze encrypted data to retrieve critical information.
8. What are the challenges faced by digital forensic investigators?
Answer: Challenges include handling encrypted or damaged data, staying updated with evolving technologies, and analyzing massive volumes of digital evidence.
9. How does digital forensics support incident response in organizations?
Answer: Digital forensics helps organizations quickly identify the source and impact of a cyberattack, recover data, and strengthen defenses to prevent similar incidents in the future.
10. What is the difference between cybersecurity and digital forensics?
Answer: Cybersecurity focuses on preventing and mitigating cyber threats, while digital forensics involves investigating incidents to uncover evidence and understand the nature of the attack.












![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)



![[2025] Top 100+ VAPT Interview Questions and Answers](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/image_100x75_6512b1e4b64f7.jpg)







