Keylogger | A Comprehensive Guide to Installation and Usage in Kali Linux
Keyloggers serve as a double-edged sword in the field of cybersecurity, showcasing their potential for both productive and malicious purposes. When used ethically, keyloggers can help in monitoring personal devices, conducting authorized security audits, or understanding potential vulnerabilities in systems. However, their misuse poses serious privacy concerns, leading to breaches of sensitive information and violation of personal rights. As cybersecurity enthusiasts or professionals, it is essential to understand not only the technical aspects of implementing such tools but also the ethical and legal boundaries that govern their use. Education and awareness about keylogger detection and prevention are equally important to safeguard systems from unauthorized monitoring, ensuring a balanced approach to leveraging this technology responsibly. Always remember, with great power comes great responsibility.

Keylogging is a fascinating aspect of cybersecurity, often explored for educational and ethical purposes such as penetration testing or system monitoring. In this blog, we'll walk through the installation, configuration, and usage of logkeys, a powerful keylogging tool, on Kali Linux. Always remember to use such tools responsibly and with proper authorization.
What is logkeys?
logkeys is a simple yet effective open-source keylogger that records keystrokes on Linux systems. It is often used for research, monitoring, or testing purposes. Its lightweight nature and ease of use make it an excellent tool for understanding how keylogging works.
Step 1: Update Your System
Before installing any tool, ensure that your system is up-to-date. This minimizes compatibility issues and ensures that all dependencies are in place.
Run the following command to update your Kali Linux system:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y
Step 2: Install logkeys
Installing logkeys is straightforward because it is included in Kali Linux’s package repositories. To install, simply run:
sudo apt install logkeys -y
This command downloads and installs the tool automatically.
Then Clone the Repository on kali Linux using git clone:
Step 3: Build Compiler
Run the following commands to compile and install logkeys:
- Initialize the build system:
- Configure the build environment:
Install the compiled binary system-wide:
Step 4: Verify Installation
After installation, confirm that logkeys is properly installed by displaying its help menu. Use the following command:
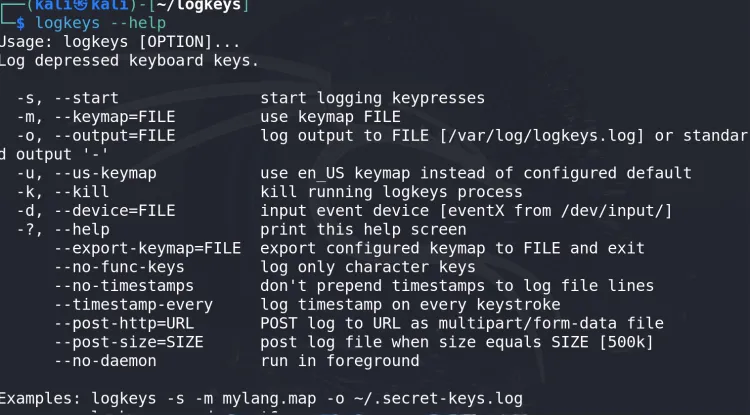
logkeys --help
If installed correctly, you'll see a list of available commands and options for logkeys.
Step 5: Start Logging Keystrokes
To begin logging keystrokes, start logkeys and specify an output file where the keystrokes will be saved. Use the following command:
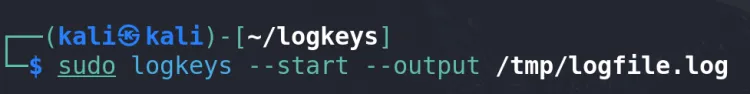
sudo logkeys --start --output /tmp/logfile.log
Replace /tmp/logfile.log with your preferred file path (e.g., /home/yourusername/logfile.log). This command initiates the keylogger, and all keystrokes will be recorded in the specified file.
Step 6: Test the Keylogger
To ensure that logkeys is working as expected:
- Open a text editor or terminal.
- Type some random text.
- The inputs will be captured and saved in the output file.
Step 7: Stop the Keylogger
When you're done testing, stop logkeys to halt further recording. Use the command:
sudo logkeys --stop
This ensures no more data is logged to the output file.
Step 8: View Captured Keystrokes
You can review the recorded keystrokes by opening the log file where the data is stored. Run the following command:
sudo cat /tmp/logfile.log
This will display all captured inputs, showcasing how logkeys records the keystrokes entered during the session.
Step 9: Clean Up After Testing
If your use case was purely educational or for testing purposes, it's good practice to clean up after yourself. Delete the log file and remove logkeys to avoid unintended consequences.
Run these commands to clean up:
sudo rm /tmp/logfile.log
sudo apt remove logkeys --purge -y
sudo apt autoremove -y
Important Notes and Ethical Considerations
- Authorization: Always ensure you have explicit permission to use keylogging tools on any system.
- Legal Compliance: Unauthorized keylogging can violate privacy laws and lead to severe legal consequences.
- Education Only: The steps above are intended solely for educational and ethical purposes.
Conclusion
Keylogging is a powerful tool in the cybersecurity professional's arsenal, but it must be used responsibly. With logkeys, you can explore the basics of keystroke monitoring on Linux systems, but always ensure respect for privacy and compliance with the law. By following this guide, you can test keylogging functionality effectively while maintaining ethical standards.
FAQ:
What is logkeys?
logkeys is an open-source keylogger designed for Linux systems. It captures keystrokes typed on the keyboard and saves them to a file. It is commonly used for educational, monitoring, and testing purposes.
2. Is using a keylogger like logkeys legal?
Using keyloggers is legal only when you have explicit authorization from the system owner. Unauthorized use of keyloggers can violate privacy laws and lead to severe legal consequences.
3. How do I install logkeys on Kali Linux?
You can install logkeys using the following command:
It is included in Kali Linux’s package repositories, so the installation is straightforward.
4. Where are the recorded keystrokes saved?
By default, you specify the output file path when starting logkeys. For example:
In this case, keystrokes will be saved to /tmp/logfile.log.
5. How can I stop logkeys from recording keystrokes?
To stop the keylogger, use the following command:
This will halt the process and stop further recording.
6. How can I verify that logkeys is working?
After starting logkeys, open a text editor or terminal and type something. Then, open the specified output file (e.g., /tmp/logfile.log) using:
You should see the recorded keystrokes.
7. How do I clean up after testing logkeys?
To clean up after using logkeys:
- Delete the log file:
- Remove
logkeysfrom your system:
8. What permissions are needed to run logkeys?
logkeys requires root privileges to run. Use sudo for all commands involving logkeys.
9. Can logkeys capture special characters or non-English inputs?
Yes, logkeys supports different keyboard layouts. If you're using a non-default layout, specify it during setup. For example:
10. What are the ethical considerations of using logkeys?
When using logkeys:
- Always obtain consent from the system owner.
- Use it only for educational, research, or authorized monitoring purposes.
- Avoid misuse, as unauthorized keylogging is illegal and unethical.














![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)








