BitLocker Explained | A Deep Dive into Windows Disk Encryption
BitLocker is a Microsoft encryption feature that safeguards data by encrypting entire drives, ensuring unauthorized users cannot access stored information. Operating at the storage layer, it works within the operating system to encrypt data while seamlessly interacting with hardware, firmware, and the OS. BitLocker leverages the Trusted Platform Module (TPM) for secure key storage and system integrity checks, supports pre-boot authentication, and encrypts data in real-time without performance impact. It protects against threats like device theft, malware attacks, and unauthorized tampering, making it a vital tool for maintaining data security and meeting compliance standards.

BitLocker is a powerful encryption feature developed by Microsoft to protect data by encrypting entire drives. It ensures that unauthorized users cannot access the stored data, even if the physical drive is removed. To understand where BitLocker operates, we need to explore the various layers of computer architecture and its role in security.
Understanding BitLocker Encryption
BitLocker is a type of full disk encryption (FDE) that operates at the storage layer of a computer system. This layer involves the operating system’s interaction with storage hardware. Let’s break down the key layers in computer architecture to pinpoint where BitLocker fits:
- Hardware Layer – Physical components like the hard disk, processor, and memory.
- Firmware Layer – Low-level software that interfaces with hardware, such as BIOS or UEFI.
- Operating System Layer – The environment where software applications and drivers operate.
- Application Layer – Software used by the end user.
- Storage Layer – Where data resides, including file systems and disk management.
BitLocker primarily operates at the storage layer, working within the operating system to encrypt data and ensure security.
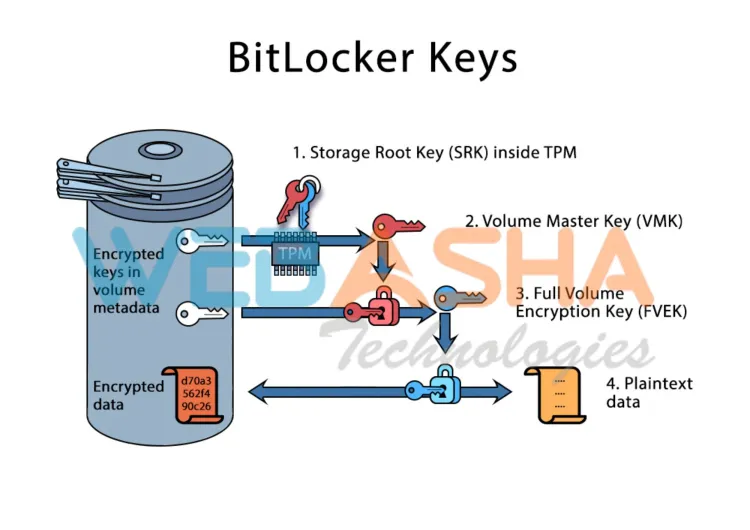
How BitLocker Works
1. Integration with the Storage Layer
BitLocker encrypts data at the block level, meaning it encrypts the entire drive, including operating system files. When the computer starts, it decrypts necessary blocks in real-time, offering seamless access to authorized users.
2. Use of Hardware-Based Security
BitLocker integrates with hardware security components, like the Trusted Platform Module (TPM), a secure cryptographic processor. The TPM works by:
- Safely storing encryption keys.
- Verifying system integrity before allowing access to encrypted drives.
3. Pre-Boot Authentication
BitLocker can require users to authenticate before the operating system boots. This can include:
- A PIN.
- A password.
- A USB key with stored credentials.
This pre-boot authentication ensures that unauthorized users cannot access the system.
4. Real-Time Encryption and Decryption
BitLocker works behind the scenes to encrypt and decrypt data as it is read from or written to the disk. This process is seamless and does not noticeably impact performance.
BitLocker’s Role in the Security Layers
BitLocker is a critical part of the data protection layer in a security model. This layer ensures the safety of stored data, protecting it from theft or tampering. BitLocker connects the hardware, firmware, and operating system layers to offer robust security.
Key Security Features of BitLocker
- Data Confidentiality – Prevents unauthorized access to the drive's contents.
- Data Integrity – Ensures system files are not altered during the boot process.
- Tamper Detection – Works with TPM to detect unauthorized changes to the system.
Why BitLocker is Important
BitLocker addresses several key threats and ensures data security in real-world scenarios:
- Device Theft – Protects data even if the physical device is stolen.
- Malware Attacks – Safeguards system-level files from ransomware and malware during boot.
- Regulatory Compliance – Helps meet standards like GDPR and HIPAA for secure data handling.
Common Misconceptions About BitLocker
1. Is BitLocker a Hardware Feature?
No, BitLocker is a software-based encryption tool, though it works closely with hardware components like TPM for added security.
2. Is BitLocker Part of the Application Layer?
Not directly. BitLocker operates at the storage layer and interacts with the operating system, not end-user applications.
3. Does BitLocker Replace Antivirus Software?
No, BitLocker protects stored data, but it does not prevent malware infections or virus attacks.
Conclusion
BitLocker operates at the storage layer, ensuring data security by encrypting entire disks and protecting against unauthorized access. Its seamless integration with the operating system, hardware, and firmware makes it a cornerstone of modern data security. By encrypting data at rest and using tools like TPM for secure key management, BitLocker provides robust protection against theft and tampering. In an era of increasing cyber threats, using BitLocker is a proactive measure to safeguard sensitive information.
Whether you are an individual user or part of an organization, enabling BitLocker is a vital step in ensuring your data remains secure.
FAQ:
1. What is BitLocker?
BitLocker is a full-disk encryption feature by Microsoft designed to protect data by encrypting the entire drive. It ensures that data remains secure from unauthorized access, even if the device is stolen or the physical drive is removed.
2. What layer of security does BitLocker operate in?
BitLocker operates at the storage layer, focusing on encrypting data on the disk. It integrates with the operating system and hardware to provide robust security.
3. How does BitLocker encrypt data?
BitLocker encrypts data at the block level of the disk using advanced encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard). It encrypts the entire drive, including system and user files.
4. What hardware is required for BitLocker to function?
BitLocker works best with a Trusted Platform Module (TPM) chip, which securely stores encryption keys and ensures the integrity of the system during the boot process. However, it can also work without TPM by requiring a USB startup key or password.
5. Does BitLocker affect system performance?
BitLocker encrypts and decrypts data in real-time, which may cause a slight performance impact. However, on modern hardware, the impact is negligible and unnoticeable during typical use.
6. Can I use BitLocker on external drives?
Yes, BitLocker includes a feature called BitLocker To Go, which encrypts external storage devices such as USB flash drives and external hard drives.
7. What happens if I lose the BitLocker recovery key?
If you lose the recovery key, you may not be able to access the encrypted data. It is crucial to back up the recovery key in a safe location, such as a Microsoft account, printed document, or secure external drive.
8. Does BitLocker protect against malware or viruses?
No, BitLocker secures data at rest by encrypting the disk but does not protect against malware or viruses. You need separate antivirus software to protect against these threats.
9. Can I enable BitLocker without administrative privileges?
No, enabling BitLocker requires administrative rights on the device. Only users with administrative access can configure BitLocker settings.
10. Is BitLocker suitable for compliance with data protection laws?
Yes, BitLocker helps organizations meet data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, and others by ensuring that sensitive data remains encrypted and inaccessible in case of theft or unauthorized access.











![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)



![[2025] Top 100+ VAPT Interview Questions and Answers](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/image_100x75_6512b1e4b64f7.jpg)







